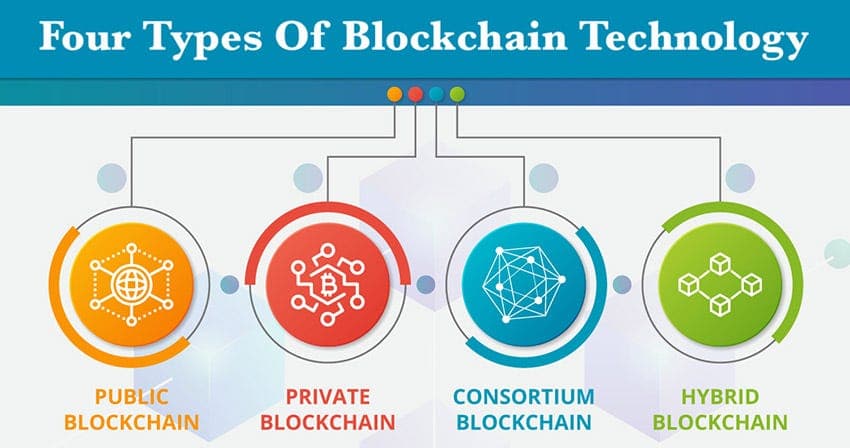
Blockchain technology is transforming a number of industries by providing a wide range of solutions that improve security, operational efficiency, and transparency. Blockchain designs can be broadly classified into four categories: consortium, public, private, and hybrid. Every kind has distinct qualities and is designed for particular uses and situations. In this piece, we will examine the key traits and real-world uses of every blockchain variation, clarifying their importance and usefulness within the current technological framework.
Explanation: Public blockchains
These open blockchains are available to every consumer without any obstacles. These solutions fully support complete decentralization because they don’t require invitations or prior approvals for participation. Thanks to this platform, anyone can take part in validating transactions or managing and expandаing the network.
- Accessibility: These blockchains are open to anyone who wishes to participate. Without requiring specific permissions, anyone can become part of the network and participate in verification and maintenance.
- Transparency:Every user on the network has access to view the public network, which records transactions. Full and absolute transparency of transactions is guaranteed, which can be verified by any interested user.
- Security: In public blockchains, data security is safeguarded using cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, which demand considerable computational effort to manipulate or corrupt the data. Decentralized distribution of devices across the network reduces the likelihood of centralized attacks.
Case Study Examples
- Bitcoin: guarantees the security of monetary transactions using this blockchain.
- Ethereum: It is a frontrunner in blockchain technology and advances the concept of public blockchains by developing a platform that facilitates the creation of diverse applications.
Exploring the Inner Workings of Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are closed, dispersed networks run by a single individual or a select few. In such systems, developers tightly control who is allowed to confirm transactions and access data. The organization that constructs the digital ledger fully controls transaction approval, ledger verification, and decides who specifically can participate in the system.
- Control: These are characterized by access control.The organization that builds the blockchain fully manages transaction approval , blockchain verification, and determines who exactly participates in the system.
- Performance: Compared to public ledgers, private ledgers can process transactions at significantly faster speeds due to the involvement of fewer participants. For business applications where performance is crucial, this efficiency is perfect.
- Privacy: Data on a private blockchain is kept private, visible to authorized network users only, and shielded from prying eyes. Enterprise applications that must strictly comply with data protection requirements need this higher level of confidentiality.
Use cases
- Hyperledger Fabric: Developed with the Linux Foundation’s assistance, Hyperledger Fabric provides a set of instruments for designing private blockchain systems that are customized to meet particular business requirements. This platform is used in sectors where complete privacy and top-notch performance are critical, such as supply chain management, healthcare, and finance.
- Corda: R3 is a provider of distributed ledger technology tailored for business applications. Corda facilitates the creation of private networks in industries like banking and finance, where transaction data is only available to the parties involved. This guarantees important privacy.
Consortium Blockchains: Harmonizing Decentralization & Regulated Access
This unique type of distributed ledger combines features of both public and private systems, overseen by various companies. It offers stringent access control and participatory rights along with decentralized management, blending the strengths of both systems. This organization guarantees high security and efficiency , making it ideal for joint ventures.
- Consistency: These blockchains have several nodes that control and validate transactions, usually on behalf of collaborating organizations. This solution ensures more dependable and consistent data administration without the influence of a single central authority.
- Scalability: This one blockchains can handle high transaction volumes with ease because of their carefully planned node count and efficient task allocation. They are perfect for large-scale industrial and commercial installations because of this capabilities.
- Security: Consortial blockchains nonetheless employ significant security mechanisms, even though they do not reach the same high security standards as public blockchains, which have thousands of independent nodes authenticating transactions. The hazards of external threats and fraudulent activities are greatly reduced by the pre-screening of participants and community administration by nodes.
Application scenarios
- R3: The financial sector is the target market for the R3 Corda stage. It provides consortium blockchains, which let businesses communicate in a highly secure & regulated setting. In addition to upholding strict privacy & data management guidelines, it is designed to conduct intricate financial operations.
- Quorum: The Quorum platform, built on Ethereum, is intended for business use and facilitates networks overseen by numerous organizations. With the addition of additional transaction control features and privacy methods, Quorum improves upon regular Ethereum functionality.
Hybrid blockchains
This advanced digital ledger system merges the advantages of both public and private ledgers. It is designed to provide individuals and organizations with the option to choose between privacy and transparency, depending on their unique needs. These blockchains combine the advantages of both approaches, enabling the creation of limited groups of users within broader open networks.
- Flexibility: A key benefit of hybrid blockchains is their adaptability. Organizations have the ability to determine which data remains private and which is released to the public. This capability enables an optimal equilibrium between the confidentiality of sensitive information and the transparency required by users.
- Control: These blockchains provide businesses total control over who can access data within the ledger. This authority includes the ability to choose which nodes in the network can engage in transaction approval and to set limitations on accessing specific data segments.
- Security and transparency: Merge the strong security measures of private blockchains, such as controlled access and authentication processes, with aspects of public blockchains that promote transparency. This integration enables hybrid blockchains to serve multiple functions, achieving a balance between openness and reliability.
Illustrations of application scenarios
Dragonchain: is a hybrid blockchain platform where businesses can employ internal, private ledgers alongside public transaction verification. Dragonchain demonstrates how enterprises can benefit from the transparency of public ledgers while managing sensitive data securely, enhancing trust, and adhering to regulatory standards.
Hybrid blockchains offer a practical approach for organizations seeking to combine rigorous security and restricted access with the need for transparent collaboration. This technology expands the possibilities for developing secure, adaptable and productive systems that meet the unique needs of different types of businesses.